The gain control is one of the most misunderstood features of a car audio amplifier. It is often mistaken for a volume knob, leading to improper usage and potential damage to the audio system. Understanding what gain control does—and doesn’t do—can help you set up your car audio system for optimal performance without risking distortion or equipment failure.
Also, known as the amplifier sensitivity adjustment, the gain control is a tool used to match the output voltage of your head unit to the input sensitivity of your amplifier. It adjusts how much the signal going to the amp is boosted to ensure efficient operation. More importantly, when set properly, it prevents the amplifier from being overdriven. Let’s explore this critical feature and clarify some common misconceptions.
What Gain Control Is Not
Contrary to popular belief, the gain control on a car audio amplifier is not a volume control. Turning up the gain does not make your system louder. It increases the system volume relative to the output of the source unit. The maximum power produced by the amp doesn’t change.
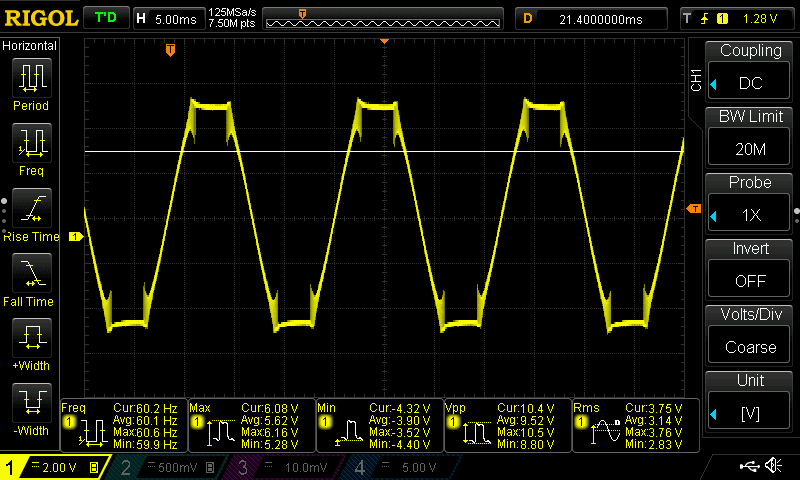
Speaking of power, another misconception is that the gain control is a power adjustment. It doesn’t regulate the power output of your amplifier; rather, it adjusts the input sensitivity to alter the balance between the head unit and the amplifier. Cranking up the gain to “increase power” is a mistake that can degrade sound quality and lead to the onset of clipping. Clipping is a form of distortion that occurs when the signal exceeds the amplifier’s capacity to reproduce it cleanly.
How Gain Control Works
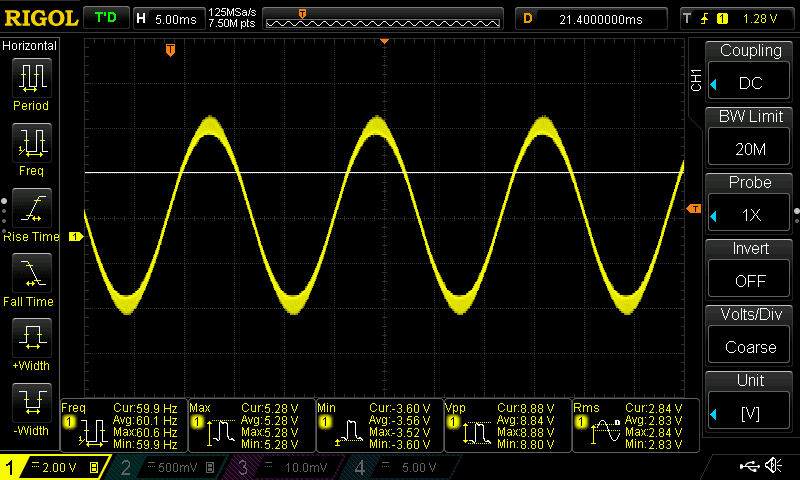
To understand how gain control works, it’s essential to know the role of input sensitivity. Amplifiers are designed to accept a range of signal strengths, typically between 0.2 and 5 volts. The gain control allows you to fine-tune the amplifier to your head unit’s specific signal strength output. If you have an inexpensive source unit that produces two volts, of maximum output, you will want the gain turned up a bit. If you have a DSP that can produce a full five volts of signal, then the amp will produce maximum power with its gain turned all the way down. This balance is critical for preserving sound quality and protecting your speakers from unnecessary strain.
Why Proper Gain Control Settings Matter
Correctly setting the gain control improves the overall sound quality of your car’s audio system. It ensures the amplifier operates within its optimal range, preventing distortion and unnecessary strain on your speakers. Most critically, proper gain adjustment can help prevent unwanted noise from being audible during quiet passages. We call this signal-to-noise ratio optimization.
Improper gain settings can lead to a host of issues:
- Distortion: Overloading the amplifier with a signal that’s too strong can produce unpleasant distortion. This distortion is full of unwanted high-frequency content that will dramatically increase the power of small speakers and tweeters, often leading to damage or complete destruction.
- Amplifier Overheating: Running the amplifier beyond its design limits due to improper gain settings can result in overheating and potential failure. At the very least, it will shorten the life of your amp.
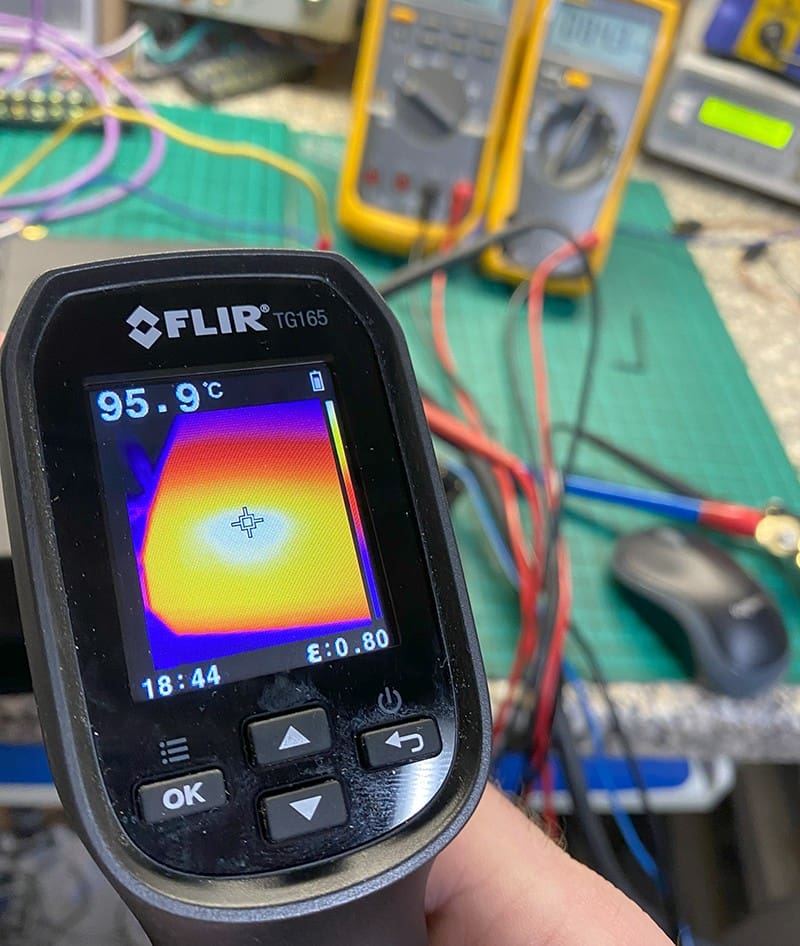

Common Gain Control Missteps
One of the most common errors made when adjusting the gain control is to use a test tone to set the level of an amp power your midrange and high-frequency speakers. If your system has a subwoofer, its best that the technician working on your vehicle starts with that. From there, the output of the rest of the system should be adjusted so that the overall balance matches a target response curve.
In most cases, systems will be capable of producing more bass than the midrange drivers can keep up with. At this point, your installer might have to back down the subwoofer level or, at the very least, ensure the amp powering the speakers can’t be driven into clipping.
Tools for Accurate Gain Control Adjustment
Investing in the right tools can make setting the gain control easier and more accurate. Here are a few helpful tools:
- Oscilloscope: This device displays the signal waveform, helping you identify clipping and distortion. This is the best tool to adjust gain controls as it can measure signal amplitude at any frequency.
- Digital Multimeter: A multimeter can measure voltage to ensure proper signal levels. However, a multimeter can’t detect distortion.
- Distortion Detectors: These tools identify the onset of distortion, allowing precise adjustments to the gain. However, most are locked to specific frequencies, which might not represent the highest amplitude signal in the system.
Trust a Professional for the Best Results
Once the gain is set correctly, it typically doesn’t need further adjustment unless your installer makes significant changes to your audio system. If you’re unsure about the suitability of the gain settings on your amplifier, consult the professional who installed and configured the system. Professional car audio installers have the expertise and tools needed to optimize your system for maximum performance. They can also ensure that all components are compatible and properly configured.
To learn more about the enhancements mentioned in this article, visit a qualified retailer near you.
Conclusion
Understanding and correctly setting the gain control on your car audio amplifier is essential for achieving clear, distortion-free sound. It’s not a volume control or a power adjustment but a tool for matching input sensitivity to the head unit’s output voltage. By avoiding common misconceptions and following proper setup techniques, you can enjoy a car audio system that sounds great and lasts for years.
This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.


Leave a Reply